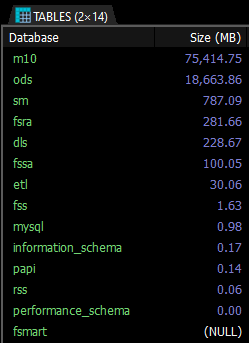
SELECT table_schema AS "Database",
ROUND(SUM(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS "Size (MB)" FROM information_schema.TABLES GROUP BY table_schema ORDER BY Size (MB) desc;
Calculate MySQL DB size
Работа с nginx + lua
nginx redis lua - record post params
Generally with payment gateways, we receive an http request to confirm a transaction. This transaction is important and the http requests must be processed. For example, we want our stack to stay available during a deployment.
Our goal is to record the payload received from a payment pingback in a Redis queue, without involving the application code.
nginx allows lua scripting with thirdparty modules lua-nginx-module.
For Redis we will use the lua-resty-redis module.
If you are on a Debian system and don't want to recompile nginx you can use the
nginx-extras and lua-nginx-redispackages.aptitude install redis nginx-extras lua-nginx-redis lua-json
Then we can create a server with this nginx config:
# on Debian the lua-nginx-redis is installed here
lua_package_path "/usr/share/lua/5.1/nginx/?.lua;;";
server {
server_name payment.local;
location / {
content_by_lua '
-- connect to redis
local redis = require "redis"
local json = require "json"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeout(1000) -- 1 sec
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
-- read post data
ngx.req.read_body()
local args = ngx.req.get_post_args()
if not args then
ngx.say("failed to get post args: ", err)
return
end
local args_to_redis = json.encode(args)
-- record it to redis
local ans, err = red:lpush("payment", args_to_redis)
if not ans then
ngx.say("failed to run rpush: ", err)
return
end
red:close()
';
}
}
Once nginx is reloaded, it can be tested with this curl command:
curl -v -XPOST \
-d "TPE=1234567&date=05%2f12%2f2006%5fa%5f11%3a55%3a23&montant=62%2e75EUR&reference=ABERTYP00145&MAC=e4359a2c18d86cf2e4b0e646016c202e89947b04&texte-libre=LeTexteLibre&code-retour=payetest&cvx=oui&vld=1208&brand=VI&status3ds=1&numauto=010101&originecb=FRA&bincb=010101&hpancb=74E94B03C22D786E0F2C2CADBFC1C00B004B7C45&ipclient=127%2e0%2e0%2e1&originetr=FRA&veres=Y&pares=Y" \
"http://payment.local/"
We can get the params, for example, on a Ruby script that parses the recorded post from nginx.
require 'redis'
require 'json'
redis = Redis.new
list, element = redis.blpop("payment")
JSON.parse(element)Источник
Дополнительные ссылки на материалы:
- Lua-nginx-module
- Мониторинг NGINX сервера с помощью Lua
- Using Lua in Nginx for unique request IDs and millisecond times in logs
- Nginx + Lua + Redis. Эффективно обрабатываем сессию и отдаем данные
- Сайт на Lua в конфигах Nginx
- Create image server with nginx + lua (Openresty) + graphicsmagick (Part I)
- Create image server with nginx + lua (Openresty) + graphicsmagick (Part II)
- handling cookies in nginx lua (open resty)
- Nginx Lua – How to modify request parameters
- Защита от ддос на Nginx с помощью модуля Lua
- Nginx на стероидах — расширяем функционал с помощью LUA
- Прозрачная авторизация сервисов в гетерогенной среде на базе Nginx/LUA
- Nginx+HTTP Lua — сборка на debian 8
- Lua script for Nginx that performs reverse proxy auth using JWT's
- Pushing Nginx to its limit with Lua
- LUA в nginx: горячий кеш в памяти
- LUA в nginx: слегка интеллектуальный firewall
- Web-Оповещения в нагруженных проектах
- Frontend на nginx+Lua
- Применение Nginx + Lua для обработки контактной формы
- https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module
- https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-redis
- http://www.londonlua.org/scripting_nginx_with_lua/slides.html
Какой то конфиг OpenVPN
#
# Sample OpenVPN configuration file for
# home using SSL/TLS mode and RSA certificates/keys.
#
# '#' or ';' may be used to delimit comments.
# Use a dynamic tun device.
# For Linux 2.2 or non-Linux OSes,
# you may want to use an explicit
# unit number such as "tun1".
# OpenVPN also supports virtual
# ethernet "tap" devices.
dev tun
server 10.208.0.0 255.255.0.0
proto udp
# 10.1.0.2 is our local VPN endpoint (home).
# 10.1.0.1 is our remote VPN endpoint (office).
ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt
push "redirect-gateway def1"
push "dhcp-option DNS BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1"
push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8"
push "reneg-sec 0"
push "rcvbuf 262144"
push "sndbuf 262144"
# Our up script will establish routes
# once the VPN is alive.
; up ./internal.routes
script-security 2 execve
client-connect /usr/local/bin/openvpn.updown.sh
client-disconnect /usr/local/bin/openvpn.updown.sh
# Diffie-Hellman Parameters (tls-server only)
dh /etc/openvpn/external-keys/dh1024.pem
# Certificate Authority file
ca /etc/openvpn/external-keys/ca.crt
# Our certificate/public key
cert /etc/openvpn/external-keys/openvpn.vpnunlimitedapp.com.crt
# Our private key
key /etc/openvpn/external-keys/openvpn.vpnunlimitedapp.com.key
# OpenVPN 2.0 uses UDP port 1194 by default
# (official port assignment by iana.org 11/04).
# OpenVPN 1.x uses UDP port 5000 by default.
# Each OpenVPN tunnel must use
# a different port number.
# lport or rport can be used
# to denote different ports
# for local and remote.
port 443
# Downgrade UID and GID to
# "nobody" after initialization
# for extra security.
; user nobody
; group nogroup
# If you built OpenVPN with
# LZO compression, uncomment
# out the following line.
comp-lzo
# The keepalive directive causes ping-like
# messages to be sent back and forth over
# the link so that each side knows when
# the other side has gone down.
# Ping every 10 seconds, assume that remote
# peer is down if no ping received during
# a 120 second time period.
ping 5
ping-restart 60
push "ping 5"
push "ping-exit 30"
#keepalive 10 120
# For extra security beyond that provided
# by SSL/TLS, create an "HMAC firewall"
# to help block DoS attacks and UDP port flooding.
#
# Generate with:
# openvpn --genkey --secret ta.key
#
# The server and each client must have
# a copy of this key.
# The second parameter should be '0'
# on the server and '1' on the clients.
;tls-auth /etc/openvpn/external-keys/ta.key 0 # This file is secret
# The persist options will try to avoid
# accessing certain resources on restart
# that may no longer be accessible because
# of the privilege downgrade.
persist-key
persist-tun
# Output a short status file showing
# current connections, truncated
# and rewritten every minute.
status openvpn-status-udp-443.log 10
# By default, log messages will go to the syslog (or
# on Windows, if running as a service, they will go to
# the "\Program Files\OpenVPN\log" directory).
# Use log or log-append to override this default.
# "log" will truncate the log file on OpenVPN startup,
# while "log-append" will append to it. Use one
# or the other (but not both).
log-append /var/log/openvpn-external-udp-443.log
# Send a UDP ping to remote once
# every 15 seconds to keep
# stateful firewall connection
# alive. Uncomment this
# out if you are using a stateful
# firewall.
; ping 15
# Uncomment this section for a more reliable detection when a system
# loses its connection. For example, dial-ups or laptops that
# travel to other locations.
; ping 15
; ping-restart 45
; ping-timer-rem
; persist-tun
; persist-key
# Verbosity level.
# 0 -- quiet except for fatal errors.
# 1 -- mostly quiet, but display non-fatal network errors.
# 3 -- medium output, good for normal operation.
# 9 -- verbose, good for troubleshooting
verb 3
# Silence repeating messages. At most 20
# sequential messages of the same message
# category will be output to the log.
mute 20
management /var/run/openvpn-udp-443.sock unix
#management 127.0.0.1 9868
reneg-sec 0
rcvbuf 262144
sndbuf 262144
Подписаться на:
Комментарии (Atom)